Vetra Studio
Introducing Vetra Studio
Vetra Studio is the builder environment where you create, manage, and collaborate on Powerhouse packages. It consists of two main components:
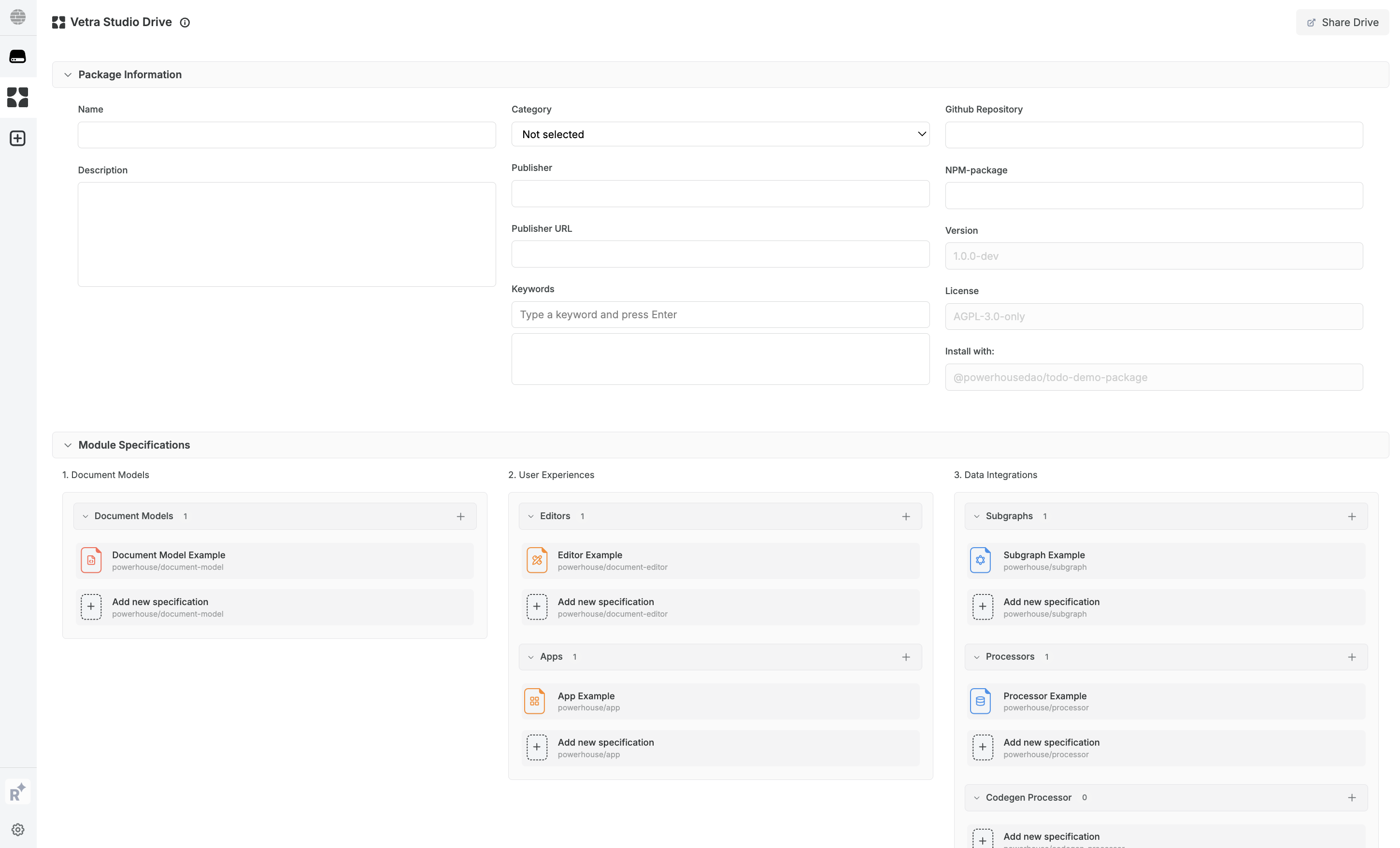
- Vetra Studio Drive: Serves as a hub for developers to access, manage & share specifications through a remote Vetra drive. It functions as the orchestration hub where you as a builder assemble all the necessary specifications for your intended use-case, software solution, or package. Each specification document corresponds to a module — a distinct building block of your package (such as a document model, editor, or data integration).
- Vetra Package Library: Store, publish, and fork git repositories of packages in the Vetra Package Library.
Visit the Vetra Package Library here
A specification document is a configuration file that defines how a specific module in your package should behave. Think of it as a blueprint — it describes the structure, rules, and relationships that Powerhouse uses to generate the actual code for that module. These specification documents unlock Specification Driven Design & Development—enabling you to communicate your solution and intent through a structured framework designed for AI collaboration. Specs serve as a shared language that enables precise, iterative edits—turning messy intent into clean execution, and turning business needs into maintainable functionality.
As Vetra Studio matures, each of these specification documents will offer an interface by which you as a builder get more control over the modules that make up your package. For now, the specification documents offer you a template for code generation.

Module Categories
1. Document Models
A document model is a structured data type that defines what information your application can store and how it can be modified. Unlike traditional databases, document models use operations (actions like "add item" or "update title") rather than direct data manipulation, making them ideal for collaborative and auditable applications.
- Document model specification: Defines the structure and operations of a document model using GraphQL SDL (Schema Definition Language), ensuring consistent data management and processing.
2. User Experiences
- Editor specification: Outlines the interface and functionalities of a document model editor, allowing users to interact with and modify document data.
- Drive-app specification: Specifies the UI and interactions for managing documents within a drive, providing tailored views and functionalities.
3. Data Integrations
- Subgraph specification: Details the connections and relationships within a subgraph (a subset of your data exposed via a GraphQL API), facilitating efficient data querying and manipulation.
- Codegen Processor Specification: Describes the process for automatically generating code from document model specifications, ensuring alignment with intended architecture.
- RelationalDb Processor Specification: Defines how relational databases are structured and queried, supporting efficient data management and retrieval.
Configure a Vetra Drive in Your Project
You can connect to a remote Vetra drive instead of using the local one auto-generated when you run ph vetra (where ph is short for "powerhouse", the CLI tool and the Organization behind Vetra).
- Without the
--remote-driveoption: Vetra will create a local drive for you that lives in your browser's local storage. This is useful for solo development or experimentation. - With the
--remote-driveargument: Vetra will connect to a remote drive instead of creating a local one. The remote drive can be hosted wherever you want (e.g., on your own server or a shared team environment).
The Powerhouse config includes a Vetra URL for consistent project configuration across different environments.
vetra: {
driveId: string;
driveUrl: string;
};
Imagine you are a builder and want to work on, or continue with a set of specifications from your teammates.
You could then add the specific remote Vetra drive to your Powerhouse configuration in the powerhouse.config.json file to get going:
"vetra": {
"driveId": "bai-specifications",
"driveUrl": "https://switchboard.staging.vetra.io/d/bai-specifications"
}
An example of a builder team building on the Powerhouse Vetra Ecosystem and its complementary Vetra Studio Drive specifications for the different packages can be found here.
📦 Vetra Remote Drive Commands
Remote drives enable collaborative development by syncing specifications across team members.
Key Commands:
ph init --remote-drive <url>- Create a NEW project connected to a remote driveph checkout --remote-drive <url>- Clone an EXISTING project from a remote driveph vetra --watch- Start development with a preview drive for testing local changes
Workflows:
- Project Owner:
ph init --remote-drive→ Create GitHub repo → Push →ph vetra --watchto configure - Collaborator:
ph checkout --remote-drive→ph vetra --watchto start developing
Preview Drive (--watch mode):
The preview drive allows you to safely test changes before they affect the shared remote drive.
- The main "Vetra" drive syncs with the remote and contains the stable package configuration.
- The "Vetra Preview" drive is created locally for testing document models and editors before syncing your changes to the team.
- When restarting Vetra, always use
ph vetra --watchso it loads your local documents and editors.